Assembly of cyclic hydrocarbons from ethene and propene in acid zeolite catalysis to produce active catalytic sites for MTO conversion
Abstract
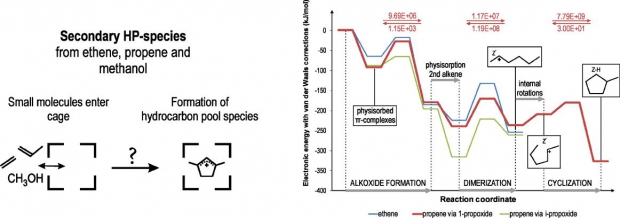
The formation of cyclic hydrocarbons from smaller building blocks such as ethene and propene is investigated in protonated ZSM-5, using a 2-layered ONIOM(B3LYP/6-31+g(d):HF/6-31+g(d)) approach and an additional Grimme-type van der Waals dispersion correction term to account for the long-range dispersion interactions. These cyclic species form precursors for active hydrocarbon pool species and play a key role in activating the acidic zeolite host for successful methanol-to-olefin (MTO) conversion. Starting from trace amounts of ethene and propene that are formed during an initial induction period or during the active phase, dimerization reactions allow for rapid chain growth. The products of these reactions can be neutral alkenes, framework-bound alkoxide species or intermediate carbenium ions, depending on the zeolite environment taken into account. On the basis of rate constants for successive reaction steps, a viable route toward cyclization is proposed, which starts from the formation of a framework-bound propoxide from propene, followed by dimerization with an additional propene molecule to form the 2-hexyl carbenium ion which finally undergoes ring closure to yield methylcyclopentane. This cyclic species in turn forms a precursor for either an active hydrocarbon pool compound or for deactivating coke deposit.
 Open Access version available at UGent repository
Open Access version available at UGent repository