A theoretical study on the solvated structural properties of various metalated 3-halo-1-azaallylic anions
Abstract
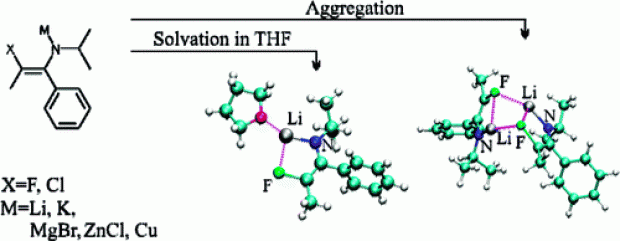
Metalated 3-halo-1-azaallylic anions are important building blocks for the preparation of a wide variety of heterocyclic and highly functionalized compounds. A theoretical description of the structural properties of halogenated 1-azaallylic anions in vacuo and in tetrahydrofuran (THF) solution is presented to gain insight into their reactivity behavior. The configurational flexibility of fluorinated and chlorinated 1-azaallylic anions is examined, and it is shown that these anions have far less configurational flexibility as compared with nonhalogenated analogues, with a strong preference to occur as Z/anti isomers. In addition, the driving force for transmetalation, that is, the replacement of the lithium cations with K+, Cu+, ZnCl+, CuCl+, or MgBr+ is studied. To obtain reliable results, the structures were modeled in THF using the combined implicit/explicit solvent approach resulting in different coordination numbers for lithium in the Z/anti and E/anti isomers. Calculations on dimerization energies show that coordination with THF is energetically preferred over aggregation.