Developing new iron-nitrogen steels with ab initio thermodynamics
Developing new iron-nitrogen steels with ab initio thermodynamics
Promotor(en): S. Cottenier, L. Duprez /18MAT03 / Solid-state physicsDeveloping new steels is one of the most important driving forces for advancements in construction, medicine and the automotive industry. A promising approach is to add nitrogen. In conventional steel processing, nitrogen alloying is challenging due to its limited solubility during casting and solidification. Alternatively, nitriding as thermochemical treatment on the final material can be used to significantly improve surface and bulk properties. By studying the Fe-N metallurgy with quantum physical simulation software, the aim is to gain a good understanding of the mechanisms of nitrogen diffusion, precipitation and the interactions with other alloying elements. The translation of this fundamental knowledge could help in the development of new breakthrough steel metallurgies based on the Fe-N system. You will be closely involved in a PhD project on iron-nitrogen steels. This project is funded and guided by OCAS NV, a market-oriented research center that produces the experimental material.
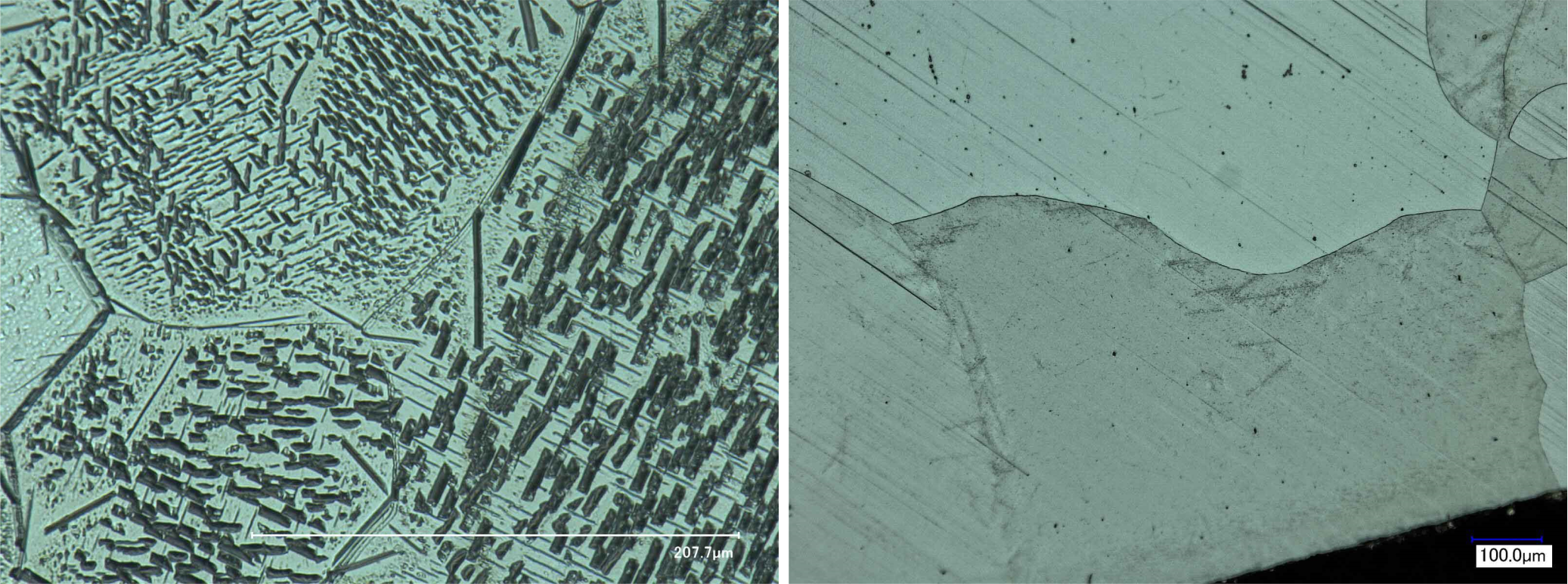
Figure 1: Left: Nitrogen is precipitated out of the Fe matrix in the form of Fe4N (slower cooling rate). Right: Nitrogen is in solid solution in the Fe matrix (faster cooling rate).
Goal
a) Computational
Calculations on the electronic level require a quantum mechanical treatment. Density-functional theory (DFT) enables us to model any Fe-N material without experimental input (ab initio). This yields the materials properties at zero kelvin. To extend these to finite temperatures, we use the quasiharmonic approach. Phonon spectra are derived from DFT calculations at different volumes, which accounts for thermal expansion, from which the vibrational contribution to the free energy can be derived. Because steels are magnetic materials, we need to take into account the magnetic entropy as well. This can also be done with DFT, by calculating the magnetic exchange interactions between atoms. All of these elements will add up to a fully ab-initio thermodynamic picture of compounds relevant for the iron-nitrogen steels. These can be used to obtain relative phase equilibria[Figure 2 (left)], a solvus, or simply the heat capacities [Figure 2 (right)].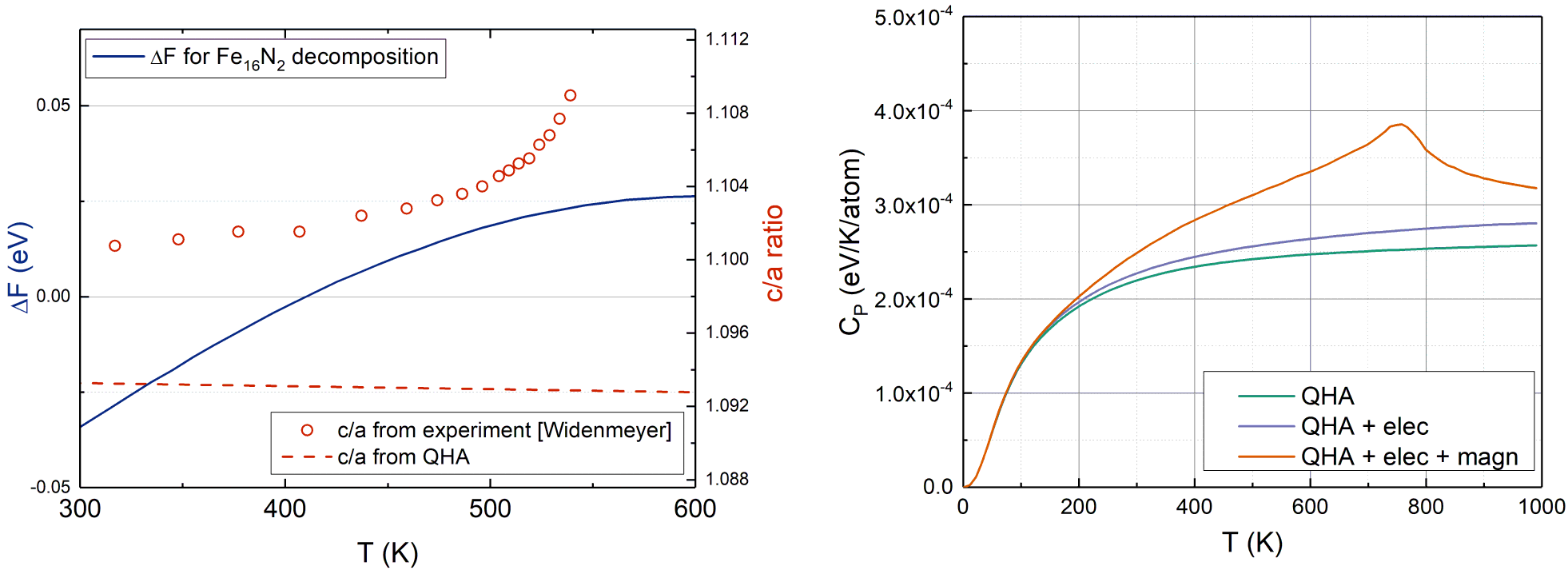
Figure 2: Left: Fe16N2 dissociation in Fe4N and Fe[N] above 400K (blue line), this coincides with a loss of crystallinity in Fe16N2 (red symbols). Right: Heat capacity of bulk Fe4N, with all relevant contributions to finite temperature. The peak in magnetic heat capacity shows the second-order phase transition from the ferromagnetic to the paramagnetic state.
At this point, we have succeeded in calculating the thermodynamic properties, such as free energy and heat capacity, for Fe with N in solid solution, Fe4N and Fe16N2. Now, we wish to expand the ab initio modeling to more complex alloys. Three possible thesis work plans are listed below, but your input is welcome as well.
• The interactions between the interstitial N and substitutional ternary elements will determine much of the alloying effect. Calculating the defect-defect interaction can be done with supercells. These supercells can subsequently be used to extend the interaction energy to finite temperatures. By comparing different alloying elements, we may understand the properties of the Fe-N steels and optimize them for use in applications.
• Taking into account the disorder that will be present when a second alloying element is added is quite a challenge. Both the vibrational and magnetic entropy become much more difficult to calculate because of it. Two methods that have gained notable interest in the last couple of years to tackle this problem are the itinerant coherent potential approximation (ICPA) and the band unfolding method. The goal is to select one or both of these methods and apply it to a well-known ternary compound, for example Fe4-xNixN, and investigate the phonon spectra, magnetisation and free energy. Comparison to a traditional supercell approach will learn to what extent disorder plays a role in Fe-N alloys.
• Fe3N1+y is often precipitated in non-equilibrium crystallographic form. Y has a very wide range (-0.40 < y < 0.48) depending on the nitrogen concentration and cooling procedure. The energetic cost of this off-stoichiometry can be investigated by calculating the vacancy and interstitial formation energy with DFT at finite temperatures. Off-stoichiometry of precipitates is a very important topic in metallurgy. A successful ab initio treatment of Fe3N1+y would be a significant advancement.b) Experimental
If it interests you, access to iron-nitrogen steel samples provides you with the opportunity to include an experimental section. The simulation of the cooling process can be investigated with salt-bath cooling, subjecting the samples to different heat treatments. Afterwards, the precipitates present in the iron matrix can be investigated with optical microscopy, electron backscatter diffraction or transmission electron microscopy. These characterization experiments, guided by professor Roumen Petrov and Vitaliy Bliznyuk, can help uncover the orientation relationship, habit planes and morphology of the precipitate phases.Aspects
Physics: Electronic structure theory, quasiharmonic approach, Curie temperature
Engineering: Fe-X-N ternary alloys. Phase diagram, experimental materials characterization (optional)
- Study programmeMaster of Science in Engineering Physics [EMPHYS], Master of Science in Sustainable Materials Engineering [EMMAEN], Master of Science in Physics and Astronomy [CMFYST]ClustersFor Engineering Physics students, this thesis is closely related to the cluster(s) MODELING, MATERIALS, NANOKeywordsdensity-functional theory, steel nitriding, quasiharmonic approximation


