Light Olefin Diffusion during the MTO Process on H-SAPO-34: a Complex Interplay of Molecular Factors
Abstract
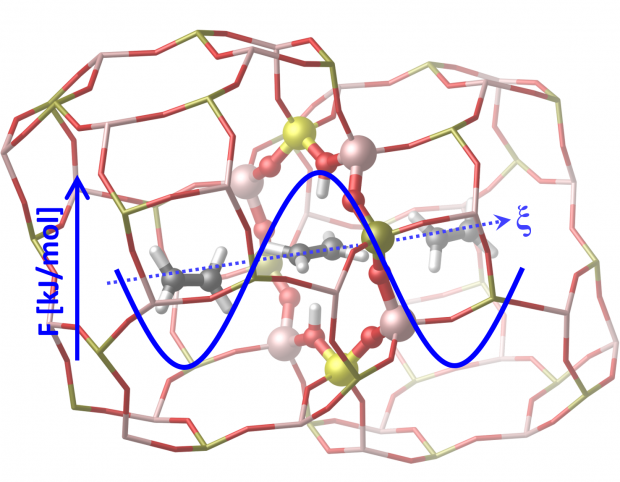
The methanol-to-olefins process over H-SAPO-34 is characterized by its high shape selectivity toward light olefins. The catalyst is a supramolecular system consisting of nanometer-sized inorganic cages, decorated by Brønsted acid sites, in which organic compounds, mostly methylated benzene species, are trapped. These hydrocarbon pool species are essential to catalyze the methanol conversion but may also clog the pores. As such, diffusion of ethene and propene plays an essential role in determining the ultimate product selectivity. Enhanced sampling molecular dynamics simulations based on either force fields or density functional theory are used to determine how molecular factors influence the diffusion of light olefins through the 8-ring windows of H-SAPO-34. Our simulations show that diffusion through the 8-ring in general is a hindered process, corresponding to a hopping event of the diffusing molecule between neighboring cages. The loading of different methanol, alkene, and aromatic species in the cages may substantially slow down or facilitate the diffusion process. The presence of Brønsted acid sites in the 8-ring enhances the diffusion process due to the formation of a favorable π-complex host–guest interaction. Aromatic hydrocarbon pool species severely hinder the diffusion and their spatial distribution in the zeolite crystal may have a significant effect on the product selectivity. Herein, we unveil how molecular factors influence the diffusion of light olefins in a complex environment with confined hydrocarbon pool species, high olefin loadings, and the presence of acid sites by means of enhanced molecular dynamics simulations under operating conditions.

 Open Access version available at
Open Access version available at